SDLC - Software Development Life Cycle
- Kunal Patil

- Mar 29, 2021
- 2 min read
Updated: Apr 20, 2021
"I wish I had more time" is something I too often say. I feel like it's something every developer can say. That's why professional developers go into their projects with a plan. This plan helps developers produce high quality software in a practical, efficient, and timely manner.
SDLC is a process followed for a software project. It consists of a detailed plan describing how to develop, maintain, replace and alter or enhance specific software. The life cycle defines a methodology for improving the quality of software and the overall development process.

1) Planning + Requirement Analysis
- The most important stage.
- Work with the client, understand what they want.
- Understand the audience.
- Determine the problem to be solved.
- Have a vision for the final product.
- Produce estimates of cost, time, and needed resources.
2) Finalize + Define Requirements
- Refine the vision with a more clear end goal.
- Establish a testing framework and testing plan!
TDD (Test Driven Development) approach
Identify functional requirements: what should the system do?
Business Rules
Transaction corrections, adjustments, cancellations
Administrative functions
Authentication / Authorization levels
Audit Tracking
Certification Requirements
Legal + Regulatory Requirements
Functional Requirements Examples
Authentication of a user when they try to log into the system.
System shutdown in the case of a cyber attack.
Verification email is sent to user whenever they register for the first time on some software system.
Identify non-functional requirements: how should the system do it?
Performance
Response Time
Throughput
Utilization
Scalability
Capacity
Availability
Reliability
Recoverability
Security
Environmental
Data Integrity
Usability
Non-Functional Requirements Examples
Emails should be sent with a latency of no greater than 12 hours.
Each request should be processed within 10 seconds.
The site should load in 3 seconds when the number of simultaneous users are > 10000
3) Architecture Design
Understanding how the system will look and function allows the developer to identify hardware and system requirements. In general, all is laid down in a special document: Design Specification Document (DSD).
Choose Technologies
What is your system environment?
What types of data are we dealing with?
Determine user interaction logic + input mediums
Choose a framework based on requirements & specifications
Choose Programming Languages

4) Building + Development
Every developers favorite part. Make the thing. Scratch your head at the bugs, implement creative solutions, ask the right questions, and use your resources.
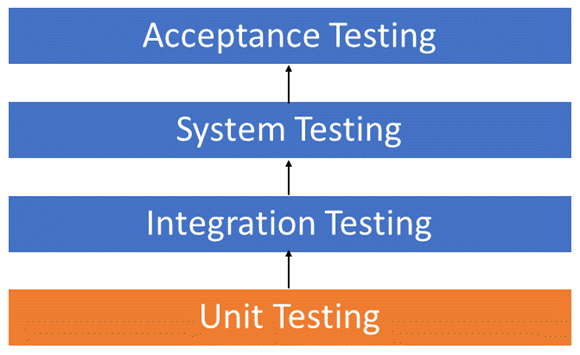
5) Testing
Every phase of the development process involves testing.
Unit Testing
Individual units or components of a software are tested.
Performed by the developers during the building + development stage
Isolate a section of code and verify its correctness.
Integration Testing
Software modules are integrated logically and tested as a group.
Exposes defects in the interaction between different software modules.
System Testing
Validates the complete product.
Evaluate the end-to-end system specifications.
Essentially a series of different tests which exercise the full system.
User Acceptance Testing
Verification and Validation from Barry Boehm:
Verification is "Are we building the product right?"
Validation is "Are we building the right product?"
6) Market Deployment + Maintenance
When customers begin utilizing the finished product in real life, various problems occasionally appear, which need to be dealt with in order to maintain the system performance. Sometimes technical support of the system is needed in order to keep up with emerging technologies and modern standards.
Conclusion
The software development life cycle can assure a high quality project with minimal resource cost. These SDLC stages are used in all development approaches, only differing in their sequence and duration. By following these steps, the client and target will get exactly what they want to.






Comments